HISTORY OF THE GOTTSCHEERS
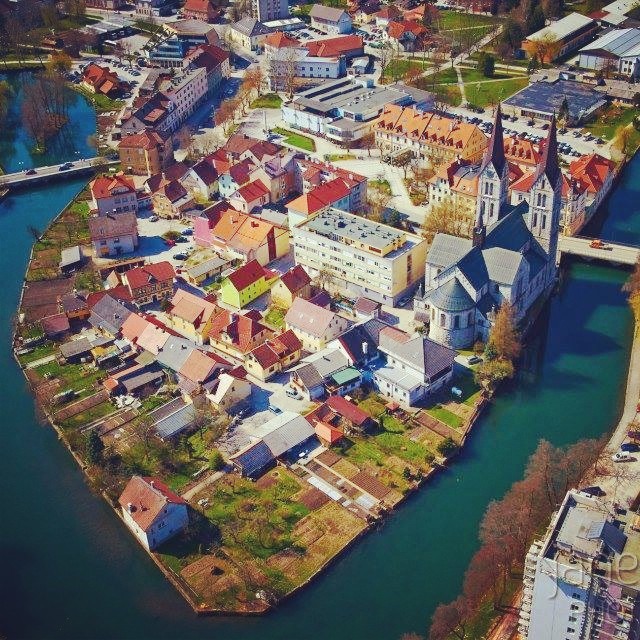

Gottscheers are the German settlers of the Kočevje (aka Gottschee) region of Slovenia, formerly Gottschee County. Until the Second World War, their main language of communication was Gottscheerish, aBavarian dialect.
They first settled in Carniola around 1330 from the German lands of Tyrol and Carinthia and maintained their German identity and language during their 600 years of isolation. They cleared the vast forests of the region and established villages and towns. In 1809, they resisted French occupation in the 1809 Gottscheer Rebellion. With the end of the Habsburg Monarchy in 1918, Gottschee became a part of the new Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Gottscheer thus went from being part of the ruling ethnicity of Austria-Hungary (and the ruling group in the estates of the province of Carniola itself) to an ethnic minority in a large Slavic state. With the onset of the Second World War and the Invasion of Yugoslavia their situation was worsened further.
While some of the Gottscheer community leaders had embraced Nazism and agitated for “assistance” and “repatriation” to the Reich even before the German invasion in 1941, most Gottscheer had no interest in reuniting with Greater Germany or in joining the Nazis. They had been integrated into society with their Slovene neighbors, often intermarrying and becoming bilingual while maintaining their Germanic language and customs. Propaganda and Nazi ideology prevailed, however, and the Main Welfare Office for Ethnic Germans (VoMi) began planning the Gottschee “resettlement” (forced expulsion) from the Italian occupation zone to the Rann Triangle (German: Ranner Dreieck), the region in Lower Styria between the confluences of the Krka, Sotla, and Sava rivers, covering most of Gottschee.
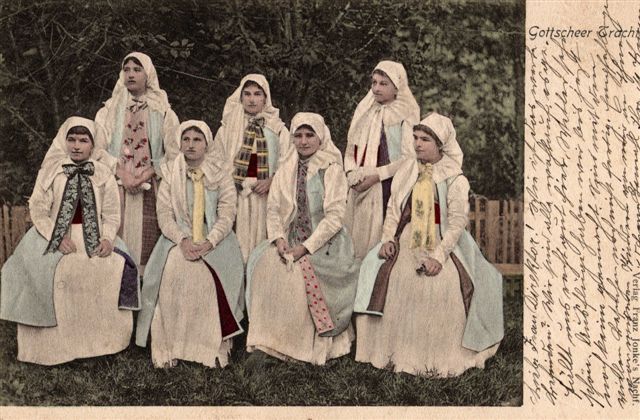



From the time of their arrival until the end of the war, Gottschee farmers were harassed and sometimes killed by partisans who saw them as an instrument of the occupying regime. The attempt to resettle the Gottscheer proved a costly failure for the Nazi regime, which needed to deploy extra manpower to protect the farmers from the partisans. The deported Slovenes were taken to several camps in Saxony, Silesia, and elsewhere in Germany, where they were forced to work on German farms or in factories from 1941-1945. The forced laborers were not always kept in formal internment, but often in nearby vacant buildings. After the end of the war, most returned to Yugoslavia to find their homes destroyed.
Now the vast majority of the Gottscheers and their descendants live in the United States, mainly in New York City and Cleveland, Ohio but also in other parts of the country. Smaller numbers have settled in Canada and Austria.
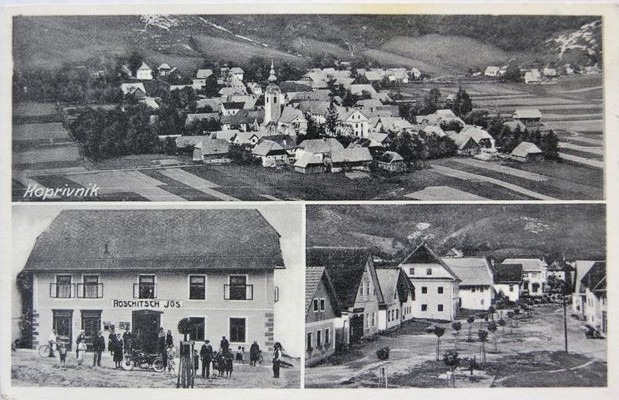

To achieve their goal, accommodation had to be made for the Gottschee settlers and, beginning in November 1941, some 46,000 Slovenes from the Rann Triangle region were deported to eastern Germany for potential Germanisation or forced labor. Shortly before that, propaganda aimed at both the Gottscheer and the Slovenes, promised the latter equivalent farmland in Germany for the land relinquished in Lower Styria. The Gottscheer were given Reich passports and transportation to the Rann area straight after the forced departure of the Slovenes. Most left their homes following coercion and threats as the VoMi had set the 31 December 1941 as the deadline for the movement of both groups. Though many Gottscheer did receive houses and farmland, inevitably there was great dissatisfaction that many properties were of lesser value and quality than their original lands, and many were in disarray after the hasty expulsion of their previous occupants.





